Chapter – 10 – More on Java
Ø Fill in the Blanks:-
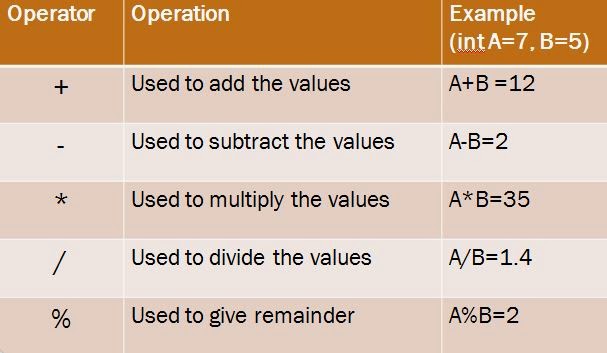
1. A symbol or function representing a
mathematical operation is called operator.
2. Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic
operation like addition,
subtraction,
multiplication, division and remainder.
3. The relational
operators compare two operands.
4. Logical operators check two or more than two
conditions.
5. If statement is used to specify condition in
the program.
6. If
..else statement is
used to handle operations when the condition is true or when it is false.
7. When there are more than two conditions to
be checked in the program, then
else .. if statement is used.
Ø Question and Answers:-
1.
Explain Arithmetic Operator.
Þ
Arithmetic
Operator to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division etc.
2.
Explain Relational or Comparison Operators.
Þ
These
operators are used to perform operations which require comparison between two
operands.
3.
Explain Assignment Operator.
Þ
Assignment
operator is used to assign value to a variable.
Example
: A=5;
means
a value 5 is assigned to the variable A
int age=15;
float marks=67.5;
char alpha=‘E’
4.
Explain Logical Operator.
Þ
When
in the program we have to specify two or more conditions, then the logical
operators are used.
5.
Explain If Statement.
Þ
It is
used to test a condition and execute a certain section of code only if the
condition evaluates to true.
Or
If statement is used when you need to
specify the condition in your program. It tells your program to execute a
certain section of code only if the specified condition evaluates to true.
Þ
Syntax :
if
(condition is true)
{
… statements to be executed
… statements to be executed
}
Þ
Example :
public class
Stud1
{
float comp=99;
float sci=100;
public void
findLargest()
{
if(comp>sci)
{
System.out.println(“Computer
marks are more than Science”);
}
}
}
Þ Output:
it will not
display anything on screen.
In
above program, the if condition holds true then the message “Computer marks are more than Science” will be
printed on the screen otherwise no message will be displayed on the screen.
6.
Explain If..else Statement.
Þ
if…else
statement is used when some action has to be taken for both cases, when the
condition is true and also when the condition is false.
Þ
Syntax :
if (condition is true)
{
… statements to be executed when condition is
true
}
else
{
… statements to be executed when condition is
false
}
Þ
Example :
public class Stud1
{
float comp=99;
float sci=100;
public void findLargest()
{
if(comp>sci)
{
System.out.println(“Computer marks are more
than Science”);
}
Else
{
System.out.println(“Science marks are more than
Computer”);
}
}
}
Þ Output:
Science marks are
more than Computer.
7.
Explain If..else..if Statement.
Þ
if…else…if statement is used when we have to check
for more than two conditions.
Þ
Syntax :
if(condition1 is
true)
{
…statements to be executed
}
else
if(condition2 is true)
{
…statements to be executed
}
else
if(condition3 is true)
{
…statements to be executed
}
else
{
…statements to be executed
}
Þ
Example :
public class
Stud1
{
float Eng=89;
float Mat=99; float Sci=70;
float Comp=86;
float SST=87;
public void
Grade()
{
float
per=(Eng+Mat+Sci+Comp+SST)/5;
char grade;
if(per>=90)
{
grade=‘A’;
}
else
if(per>=70)
{
grade=‘B’;
}
else
if(per>=50)
{
grade=‘C’;
}
else
if(per>40)
{
grade=‘D’;
}
else
{
grade=‘F’;
}
}
System.out.println(“Grade
= ” +grade);
}
Þ Output:
Grade = B.
Ø
Text Book Exercise :-
Chapter – 11 –
Computer Network
Ø Fill in the Blanks:-
1.
The
term Computer Network means
an interconnected collection of autonomous computers.
2.
The
Computer Networks are classified depending on transmission technology and scale.
3.
The
different types of networks are LAN,
WAN, MAN and Wireless Networks.
4.
Topology is the term used to describe the way
through which computers are connected in a network.
5.
A
network provides the necessary resources for data communication over the network.
6.
The data can be in the form of text, sound, video,
images, files, etc.
7.
A node
which cannot process information and no hard disk attached is called Dumb Terminal.
8.
The
LANs inside the WAN are called sub-networks.
9.
Wan
consists of a collection of machines which are called hosts.
10.
Metropolitan Area Network is
connected through Telephone lines.
11.
Wireless Network is possible through infrared, satellites
and radio waves.
12.
The
communication line through which data flows from one computer to another is
called network channel.
13. Various
types of cables like Coaxial, Fiber
Optic, Twisted Pair are used for transmission of data in a network.
Ø Question and Answers:-
1. What is a Network?
Advantages of using Network?
Ans :
The
term “Computer Network” means an interconnected collection of autonomous
computers. Any two computers are said to be interconnected, if they can
exchange information or data.
Advantages of using Network:
1.
To transfer files from one
computer to another.
2.
To share applications
software there by reducing the cost of multiple copies of the software.
3.
The various resources like
– printers, scanners, CD-ROM drives can be shared.
4.
Effective data
communication system over the network reduces the paper work. Thus it helps in
making almost a paperless office.
5.
A network enables access
to database located centrally on a server or distributed on machines.
6.
Railways and Airlines
reservation is not possible without a network of computers.
2. Components of a Computer
Network?
Ans :
1) Servers :
Servers can be mainframes, minis and micros
which can support various software, to store and process information at high
speed.
2) Nodes :
The Computers attached to the network for
the users to carry out their tasks using network and server.
Even printers, scanners etc. Attached to
the network are called nodes.
3) Workstation :
A powerful node which can handle local
information processing is called a workstation.
A workstation has a small hard disk
attached it to carryout local tasks.
4) Network Operating System :
To control all the information transfer
activities on the network, software called Network Operating System is used.
Ex: - Windows NT, Windows 2000.
5) Cables :
It is the medium or channel over which the
information travels from computer to computer.
Various types of cables viz. Coaxial, Fiber
Optic, Twisted Pair are used for transmission of data in a network.
6) Network Interface Card :
It is plugged into a computer to work with
the network operating system to control the flow of information over the
network.
7) Hubs :
They are used for extending a network to
attach additional workstation to it.
8) Switches :
They are used for forwarding data packets
directly to the parts having particular network address.
9) Repeaters :
It is an unintelligent device connecting
two network segments of same type. It moves the signals from one network
segment to another by regenerating, re-timing and amplifying it.
10) Bridges :
It is used to connect two groups of
computer of the same type so that they can exchange data.
11) Routers :
They are intelligent connecting devices
which are used to send packets to the correct local area network segments and
finally to their destination.
12)
Gateways :
These are shared network connections between local area
networks and wide area networks. Internet Service Provider (ISP) are gateway
nodes.
3. Types of Network? Explain.
Ans:
Computer networks are
classified depending on transmission technology and scale.
Different types of
networks are:
1.
Local Area Network (LAN)
2.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
3.
Metropolitan Area Network
(MAN)
4.
Wireless Network
( also refer page no : 114
from textbook )
1. What is a
topology? Explain different types of topologies.
The physical arrangement of
the cables, computers and other peripheral devices to form a network is known
as a topology
Ex – Linear Bus topology or
Bus topology, Star topology, Ring topology,
Tree topology
1.
Bus
topology – Bus topology is made up of
a main single cable with the terminators at the both ends. Computers and other
devices including the server are connected to this linear cable for
communication.
Advantage:
Easy to add or remove any
node to this network.
Disadvantage:
In case of break in main
cable whole network can shut down.
2.
Star
topology – Star topology is the most
common topology used. All the workstations are connected to the central
connection point calls a hub. Any
data sent to the other computer, first goes to the central hub and from there
it is redirected to the destination computer.
Advantage:
Easy to install and cabling and easy to
detect faults and
If any node gets broken network does not shut
down.
Disadvantage:
More expensive & require more cable
length.
3.
Ring
topology – In a ring topology, every
workstation has exactly two neighbors for communication purpose. All messages
travel through a ring in the same direction either ‘clockwise’ or
‘anticlockwise’.
Advantage:
It
cannot have any routing problem as data will be received by every node.
Disadvantage:
If
a single connection gets broken whole network can shut down.
4.
Tree
topology – It is a combination of
linear bus and star topology. It consists of groups of star configured
workstation connected to a linear bus back bone cable.
Advantage:
The point to
point wiring for individual segments.
Disadvantage:
It
is difficult to configure and wire than any other topology.
( also refer page no : 115
to 117 from textbook )
Ø Exercise:-
for better exam preparation also refer textbook and work book along with this material.








.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment